This set of exercises is not fully ready and will be improved over the next few days. Do at your own risk ;)
Programming exercise
These exercises should help you write faster, more efficient code. So this exercises are inspired by both your LOGO code and mine (https://hubiatgit.github.io/Starting_Github/LOGO/LOGO_Hubi.html ).
Goal: Improve the performance of the code below by creating more efficient functions.
Data frame for testing the speed
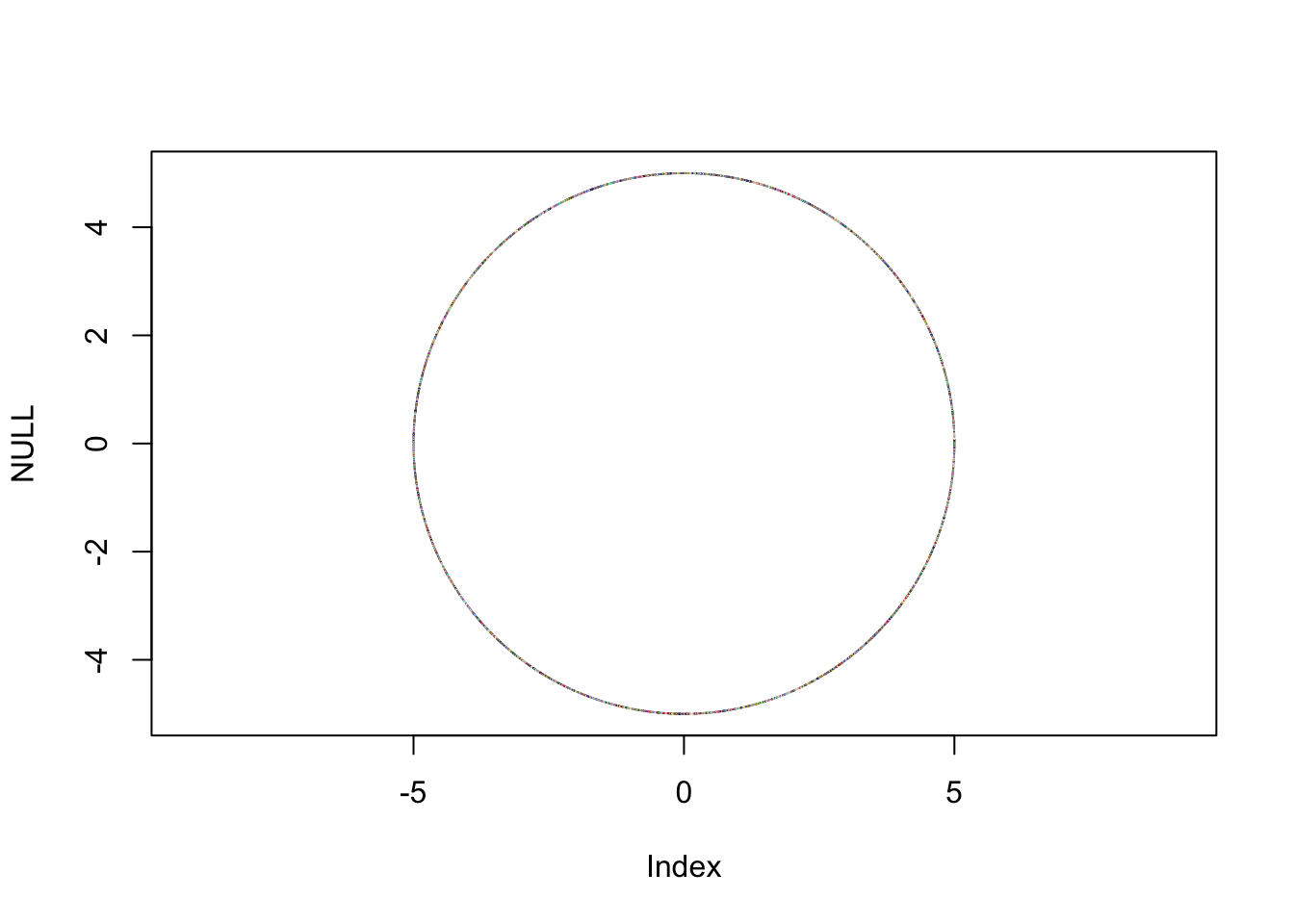
<- data.frame (angle = seq (0 , 360 , 0.1 ))$ x <- 5 * cos (hist$ angle / 180 * pi )$ y <- 5 * sin (hist$ angle / 180 * pi )$ color <- sample (colors (), size = nrow (hist), replace = TRUE )$ color[sample (1 : 50 , 1 )] <- "red" head (hist)
angle x y color
1 0.0 5.000000 0.000000000 royalblue1
2 0.1 4.999992 0.008726642 darkslategray3
3 0.2 4.999970 0.017453257 peru
4 0.3 4.999931 0.026179819 blueviolet
5 0.4 4.999878 0.034906301 grey59
6 0.5 4.999810 0.043632677 green3
1. Constants
Doing things only ones if possible, means pre calculate often used numbers.
<- function (x, y, hist) {<- hist$ x[[length (hist$ x)]] + 2 / 3 * cos (hist$ angle[nrow (hist)] * (pi / 180 ))<- hist$ y[[length (hist$ y)]] + 2 / 3 * sin (hist$ angle[nrow (hist)] * (pi / 180 ))return (c (new_x, new_y))new_pos (10 , 3 , hist)
[1] 5.666667e+00 -1.387933e-15
Speed-test:
:: mark (slow = new_pos (10 , 3 , hist),fast = new_pos_fast (10 , 3 , hist)
# A tibble: 2 × 6
expression min median `itr/sec` mem_alloc `gc/sec`
<bch:expr> <bch:tm> <bch:tm> <dbl> <bch:byt> <dbl>
1 slow 3.81µs 4.39µs 208221. 0B 41.7
2 fast 2.17µs 2.62µs 330353. 56.4KB 66.1
2. Early returns
Stop searching as soon as you’ve found what you’re looking for. This idea can also be applied to a series of if-statements.
<- function (hist) {<- 1 <- c () while (i <= nrow (hist)) {if (hist$ color[i] == "red" ) {<- c (res, i)<- i + 1 return (max (min (res),0 ))find_first_red (hist)
Speed-test:
:: mark (slow = find_first_red (hist),fast = find_first_red_fast (hist)
# A tibble: 2 × 6
expression min median `itr/sec` mem_alloc `gc/sec`
<bch:expr> <bch:tm> <bch:tm> <dbl> <bch:byt> <dbl>
1 slow 4.71ms 4.97ms 199. 0B 81.6
2 fast 11.11µs 12.67µs 74714. 33.1KB 59.8
3. Omit Loops
Almost all functions in R can handle vector inputs. This means that loops aren’t truly avoided, but they are executed at the much faster underlying machine level.
<- function (hist) {plot (NULL ,xlim = range (hist$ x), ylim = range (hist$ y), asp = 1 )for (i in 2 : nrow (hist)) {segments (x0 = hist$ x[i - 1 ], y0 = hist$ y[i - 1 ],x1 = hist$ x[i], y1 = hist$ y[i],col = hist$ color[i])replot_hist (hist)
Speed-test:
:: mark (slow = replot_hist (hist),fast = replot_hist_fast (hist)
Warning: Some expressions had a GC in every iteration; so filtering is
disabled.
# A tibble: 2 × 6
expression min median `itr/sec` mem_alloc `gc/sec`
<bch:expr> <bch:tm> <bch:tm> <dbl> <bch:byt> <dbl>
1 slow 72.7ms 82.5ms 10.5 159KB 24.5
2 fast 24.8ms 26.2ms 37.3 639KB 0
4. Growing objects
Last but in my code possibly the worst: appending rows to an existing list or data frame using append(), c(old, new), or even rbind().
<- function (x, y , hist) {<- hist$ angle[length (hist$ angle)]<- hist$ color[length (hist$ color)]<- data.frame (angle = last_angle,x = x,y = y,color = last_color<- rbind (hist, new_row)tail (add_line (3 ,10 ,hist))
angle x y color
3597 359.6 4.999878 -3.490630e-02 mediumturquoise
3598 359.7 4.999931 -2.617982e-02 orange1
3599 359.8 4.999970 -1.745326e-02 grey59
3600 359.9 4.999992 -8.726642e-03 grey38
3601 360.0 5.000000 -1.224647e-15 springgreen3
3602 360.0 3.000000 1.000000e+01 springgreen3
Speed-test:
:: mark (slow = add_line (3 , 10 , hist),fast = add_line_fast (3 , 10 , hist)
# A tibble: 2 × 6
expression min median `itr/sec` mem_alloc `gc/sec`
<bch:expr> <bch:tm> <bch:tm> <dbl> <bch:byt> <dbl>
1 slow 176.8µs 225.4µs 4214. 318KB 22.7
2 fast 65.2µs 89.4µs 11037. 333KB 63.8
5. Logo
Now try to make your own Logo code faster. To begin, you might want to start by profiling your code, as described here: https://adv-r.hadley.nz/perf-measure.html
For this, you’ll need a plain R script, which you can create like this:
library (profvis)library (bench)library (knitr)# convert your file to a R Script purl ("LOGO/LOGO_Hubi.qmd" , output = "LOGO/LOGO_profiling.R" )# loading this file as a source source ("LOGO/LOGO_profiling.R" )# then run your logo inside profvis() profvis (run_LOGO ("CS SP [-pi/5] [-Sin(PI/2)/2] sPc [black] REPEAT 20 [RepeaT 180 [FD 1 RT 2] RT 18] SPEED 100 Home SpC [gREEN] StC [blue] REPEaT 20.1 [rEPEAT 180 [fD 1 RT 2] RT 18] UndoChunk CS REPEAT 150 [ FD [n * 2] RT 91 ] SPEED 1 saVe [Logo04]" ))